An electronic high pressure washer is a pressure washing system that uses an electric drive combined with electronic control and protection systems to deliver stable, regulated high-pressure water for professional cleaning applications. Unlike basic consumer electric washers, electronic high pressure washers are designed for controlled output, operational safety, and continuous or frequent use in commercial and industrial environments.
The term “electronic” does not simply describe the power source. It refers to the integration of electronic components that monitor, regulate, and protect the system during operation—ensuring consistent performance and long service life.
In an industrial context, “electronic” refers to the presence of electronic control and protection functions within the pressure washer system. These typically include:
These electronic elements help reduce pressure fluctuations, improve energy efficiency, and protect key components such as the motor and pump—especially during long or repeated cleaning cycles.
Although often used interchangeably, these terms describe different system designs:
Understanding these distinctions helps users select the right pressure washer based on application demands, duty cycle, and operating environment, rather than power source alone.
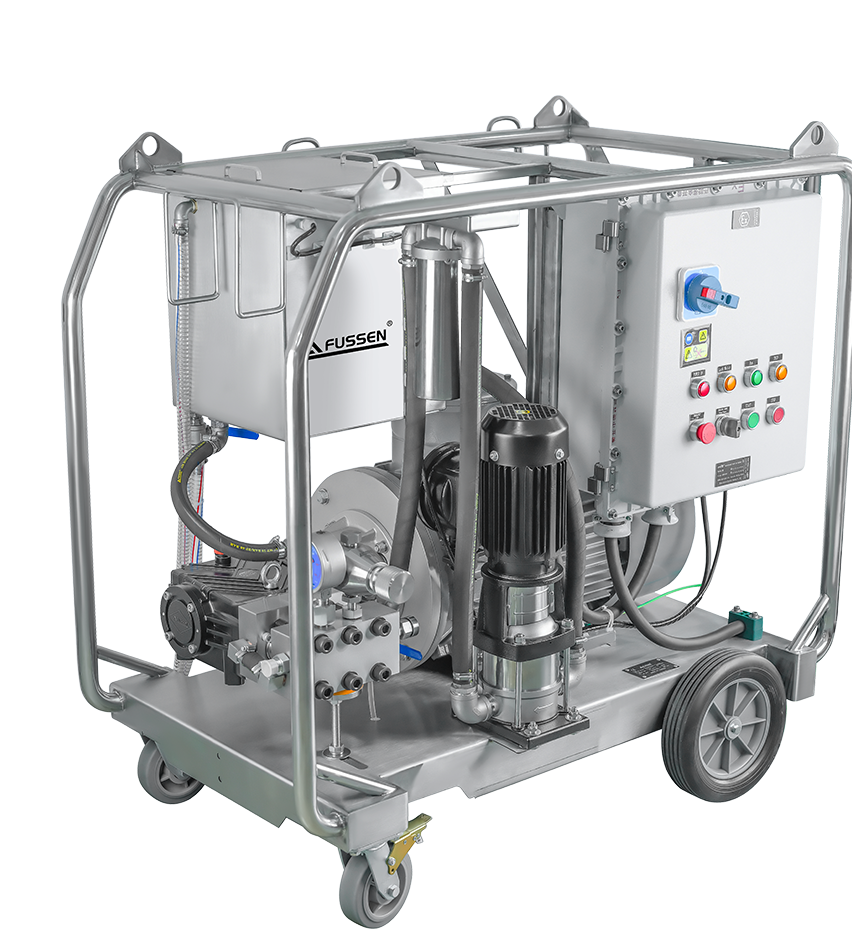



Electronic high pressure washers offer precise control, stable output, and low-emission operation—but they are not the ideal solution for every cleaning scenario. Understanding where these systems perform best, and where alternative power sources are more appropriate, helps ensure efficient cleaning and long-term reliability.
Electronic high pressure washers are particularly well suited to environments where control, consistency, and operational safety are priorities. Typical applications include:
In these applications, electronic systems provide predictable performance, reduced noise levels, and lower operating emissions compared to engine-driven machines.
Diesel or petrol pressure washers remain the preferred choice in scenarios where mobility and power independence are critical. These systems may be more suitable for:
In such cases, engine-driven pressure washers offer greater flexibility and sustained output without dependence on electrical infrastructure. Selecting the right system ultimately depends on balancing power availability, workload intensity, and operating conditions.
An electronic high pressure washer operates as an integrated system in which the electric motor, high-pressure pump, and electronic control components work together to generate and regulate cleaning power. Unlike basic electric washers, electronic systems actively monitor operating conditions to maintain stable output and protect key components during operation.
The process begins when the electric motor drives the high-pressure pump, typically a plunger pump in professional systems. Water enters the pump at low pressure and is mechanically compressed to the required working pressure.
Electronic control components manage this process by:
This coordination ensures the pump delivers consistent pressure while operating within safe mechanical and electrical limits.
Electronic control systems provide several advantages over purely mechanical regulation:
By maintaining controlled operating conditions, electronic systems improve cleaning consistency while reducing the risk of equipment failure—especially during extended or repeated cleaning cycles common in industrial and municipal environments.
The performance of an electronic high pressure washer is determined by the quality and integration of its core components. In professional systems, these components are designed to work together under continuous load, ensuring stable output, operational safety, and long service life.
At the heart of an electronic high pressure washer is an industrial-grade electric motor, typically designed for continuous or frequent operation. Unlike consumer motors, industrial motors are built with higher insulation ratings, improved cooling, and stronger bearings to handle sustained workloads.
The electronic control system manages motor operation by:
This combination ensures smooth operation, reduced energy loss, and protection against electrical and mechanical stress.
The pump is the component responsible for converting mechanical energy into water pressure. In electronic high pressure washers, plunger pumps are commonly used due to their durability and pressure stability.
Key pump considerations include:
High-quality pump selection directly impacts cleaning efficiency, maintenance intervals, and overall system reliability.
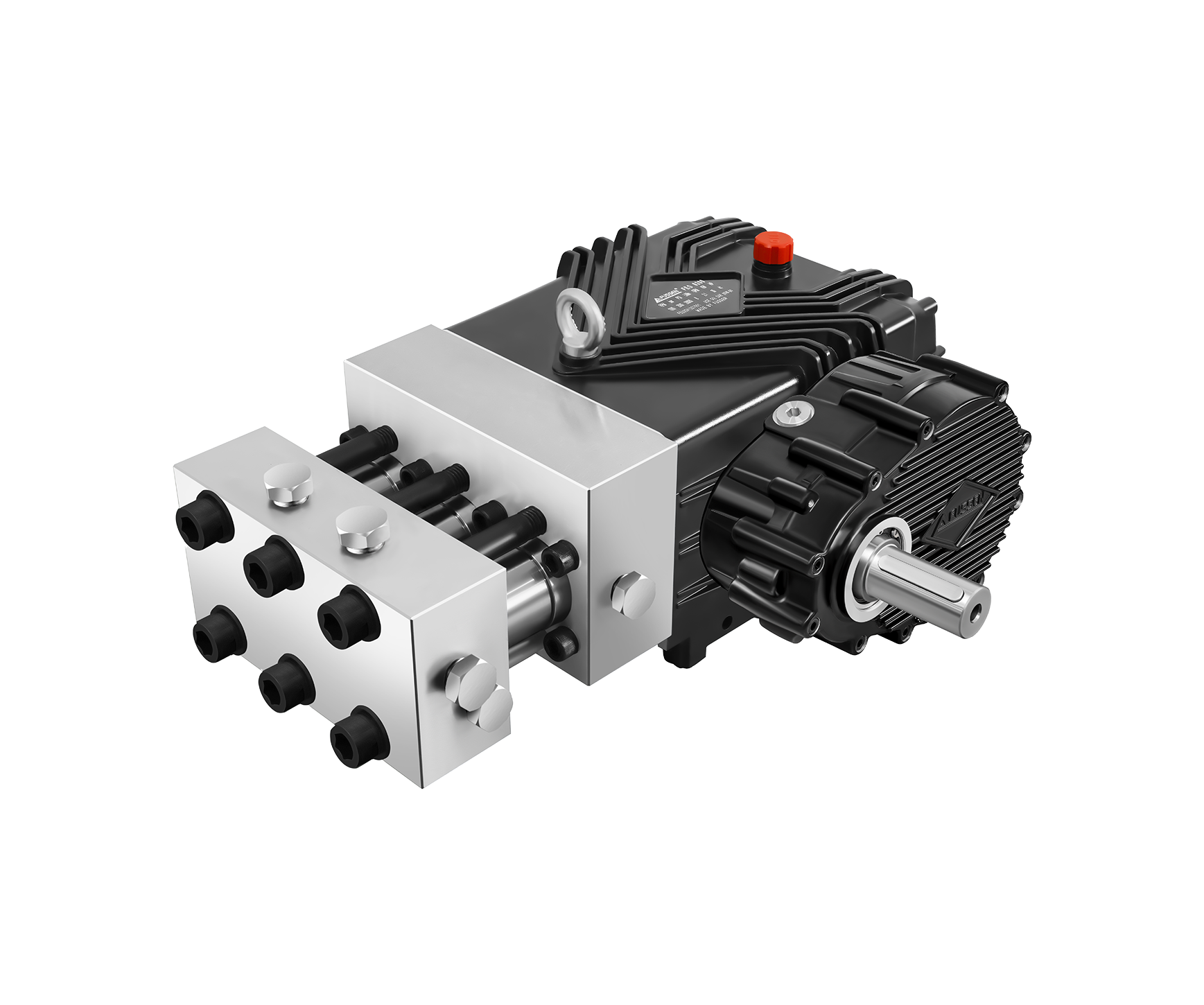



Electronic pressure washers rely on integrated safety and regulation systems to maintain controlled operation. These typically include:
Together, these components help prevent pressure spikes, reduce wear on mechanical parts, and ensure safe operation in professional cleaning environments.
Electronic high pressure washers are available in several configurations, each designed to meet different workload intensities, operating environments, and cleaning objectives. Understanding these categories helps users select equipment that delivers reliable performance without unnecessary complexity or cost.
Light-duty electronic pressure washers are designed for regular but non-continuous cleaning tasks in commercial and workshop environments. These machines prioritise ease of operation, compact design, and stable pressure output.
Typical characteristics include:
Common applications include workshop wash-down, vehicle maintenance, equipment cleaning, and general facility hygiene. These systems are well suited to environments with predictable workloads and reliable electrical supply.
Industrial electronic high pressure washers are engineered for extended operating hours and high workload intensity. These systems are built around heavy-duty components to ensure stable performance under continuous or repeated use.
Key features typically include:
These machines are commonly used in manufacturing plants, municipal maintenance, logistics facilities, and large-scale industrial cleaning operations where uptime and reliability are critical.
Hot water electronic high pressure washers integrate a water heating system to improve cleaning effectiveness where cold water alone is insufficient. By combining elevated water temperature with controlled pressure output, these systems are particularly effective for removing oil, grease, and industrial residues.
Typical use cases include:
Hot water systems may be configured on either light-duty or industrial platforms, depending on pressure, flow, and duty cycle requirements.
Understanding the typical specifications of electronic high pressure washers helps set realistic performance expectations and ensures the selected system is suited to the intended application. In professional and industrial environments, pressure, flow rate, and duty cycle must be evaluated together rather than in isolation.
Electronic high pressure washers commonly operate within a working pressure range of approximately 120–300 bar, depending on system design and application requirements.
In electronic systems, pressure stability is often more important than peak pressure values, as consistent output improves cleaning quality and protects surfaces.
Flow rate plays a critical role in determining cleaning speed and coverage area. Electronic high pressure washers typically deliver flow rates ranging from 10–30 L/min, with higher-flow systems improving efficiency on large surfaces.
A balanced pressure–flow combination ensures efficient contaminant removal without excessive water consumption.
Duty cycle defines how long a pressure washer can operate safely without interruption. Electronic high pressure washers designed for professional use are typically rated for:
Industrial-grade electronic washers incorporate reinforced motors, heavy-duty pumps, and advanced control systems to support long operating hours while maintaining stable performance and component longevity.
Selecting an electronic high pressure washer requires evaluating more than just maximum pressure figures. Professional cleaning performance depends on a balanced system design that matches real operating conditions and long-term usage requirements.
Pressure determines the impact force applied to contaminants, while flow rate controls how effectively loosened dirt is flushed away. An optimal balance between the two ensures efficient cleaning without unnecessary stress on surfaces or equipment.
For most industrial applications, increasing flow rate often delivers greater productivity gains than increasing pressure alone.
Power availability directly influences system capability and stability.
Choosing the appropriate power supply ensures stable motor operation and reduces the risk of electrical overload.
The pump is the most heavily loaded component in a pressure washer. In electronic systems, plunger pumps are commonly selected for their durability and ability to maintain consistent pressure under extended use.
Factors influencing service life include:
Selecting a system built around proven pump technology reduces downtime and long-term maintenance costs.
Electronic and diesel pressure washers serve different operational needs. Understanding their differences helps users select the most effective solution for their cleaning environment.
Noise, Emissions, and Indoor Suitability
Electronic high pressure washers operate with significantly lower noise levels and produce no exhaust emissions, making them suitable for indoor use and urban environments. Diesel systems generate higher noise and emissions and are generally restricted to outdoor or well-ventilated locations.
Output Stability and Control Precision
Electronic systems offer superior pressure stability and control precision, as electronic regulation continuously monitors operating conditions. Diesel-driven washers rely more on mechanical regulation, which may result in greater pressure fluctuation during load changes.
Operating Cost and Maintenance Differences
Electronic high pressure washers typically have lower operating costs due to reduced fuel consumption, fewer moving engine components, and simpler maintenance routines. Diesel systems offer greater mobility and independence from electrical power but involve higher fuel, servicing, and long-term maintenance costs.
Selecting between electronic and diesel systems depends on balancing power availability, workload intensity, and operational environment.
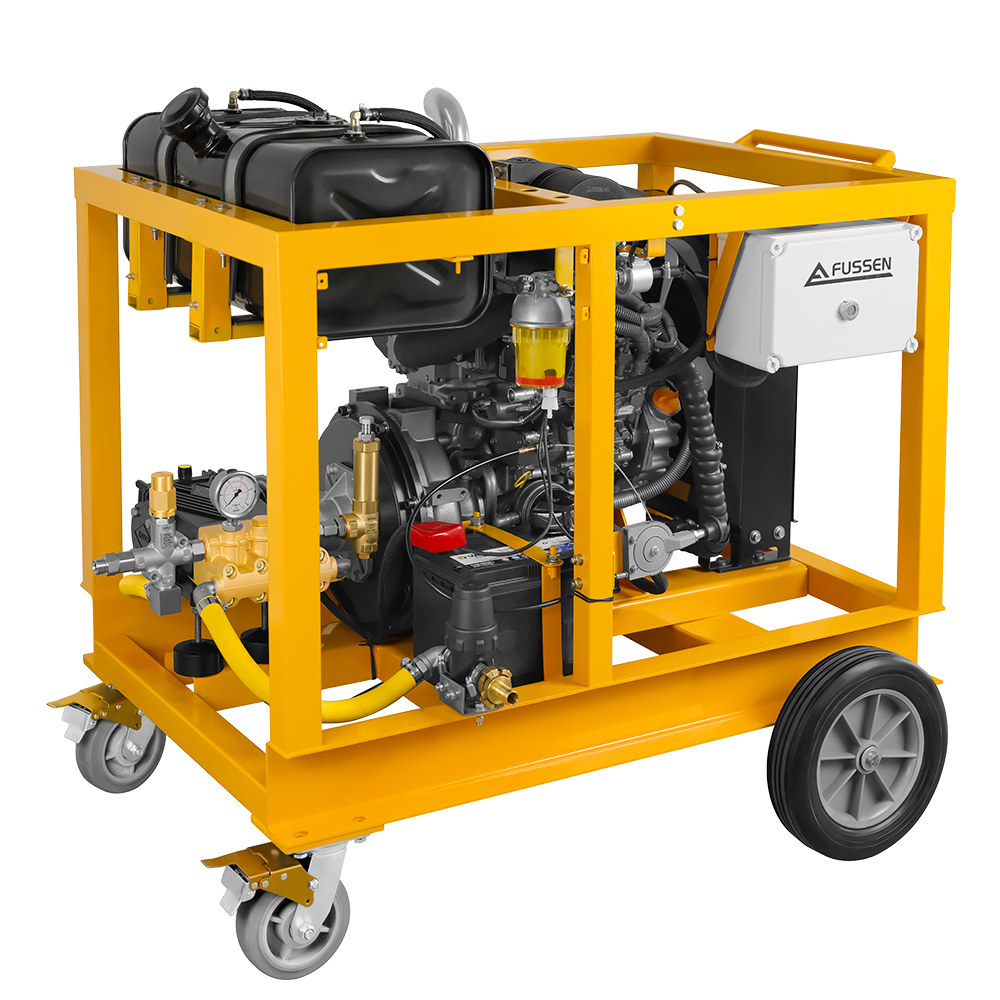
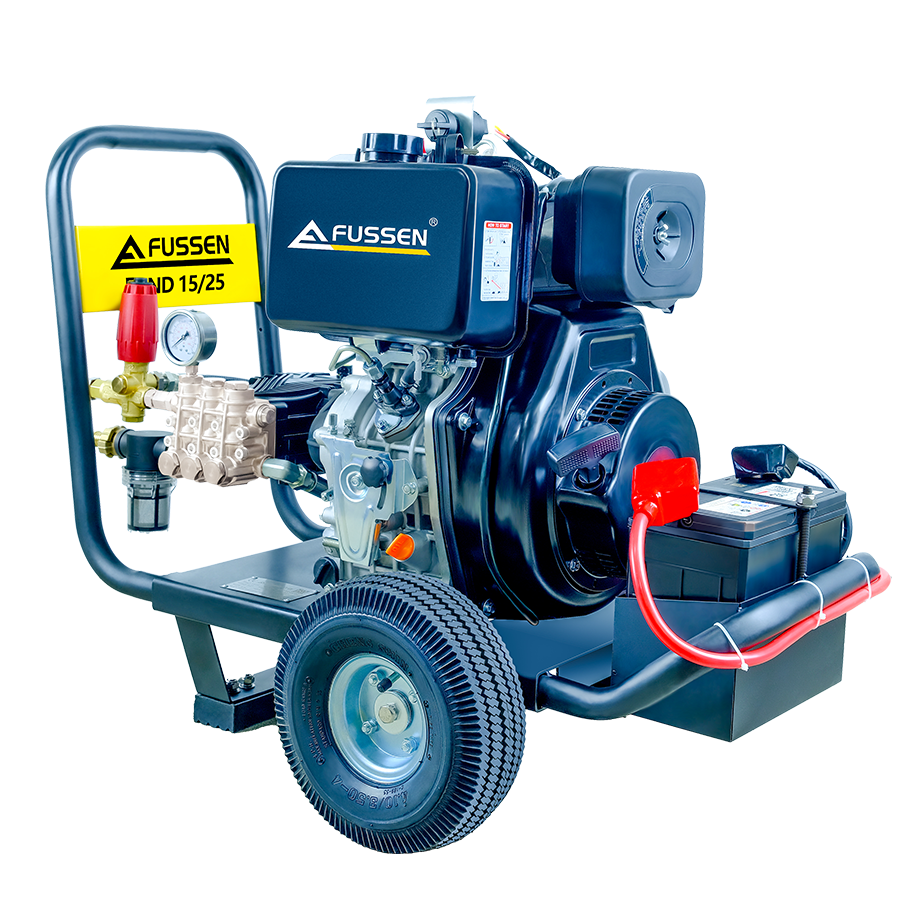


Electronic high pressure washers are widely used in professional environments where controlled performance, low emissions, and operational stability are required. Their versatility makes them suitable across a broad range of industrial and commercial applications.
In workshops and manufacturing facilities, electronic high pressure washers are commonly used for equipment wash-down, floor cleaning, and general maintenance. Stable pressure output and controlled flow help protect machinery while ensuring effective removal of dirt, dust, and production residues.
Electronic systems are well suited for cleaning cars, trucks, construction equipment, and industrial machinery. Their precise pressure control reduces the risk of surface damage, making them ideal for regular vehicle maintenance and fleet cleaning operations.
In food processing, pharmaceutical, and other hygiene-critical environments, electronic high pressure washers offer clean operation with no exhaust emissions. Combined with hot water capability where required, these systems support effective cleaning while meeting strict hygiene and safety standards.
Low noise levels and emission-free operation make electronic high pressure washers suitable for use in urban locations, enclosed spaces, and noise-sensitive environments. This allows cleaning activities to be carried out during normal operating hours without causing disruption.
Selecting the correct electronic high pressure washer involves aligning system specifications with real cleaning demands. A structured evaluation helps avoid performance issues and unnecessary operating costs.
Different cleaning tasks require different pressure and flow combinations. Higher pressure is effective for stubborn contamination, while higher flow rates improve productivity on large surfaces. Matching these parameters ensures efficient cleaning without excessive energy or water use.
Underpowered machines lead to slow cleaning and inconsistent results, while over-specified systems increase initial investment and operating costs without practical benefits. Selecting equipment based on realistic workload requirements ensures balanced performance and cost efficiency.
In professional environments, downtime directly impacts productivity. Choosing an electronic high pressure washer built with durable components and supported by reliable after-sales service helps ensure long-term performance, quick maintenance response, and reduced total cost of ownership.
Are electronic high pressure washers suitable for industrial use?
Yes. Industrial electronic high pressure washers are specifically designed for professional environments. When built with heavy-duty motors, plunger pumps, and proper electronic protection, these systems can handle frequent or continuous operation in factories, municipal facilities, and large-scale cleaning applications.
Can electronic pressure washers run continuously?
Electronic pressure washers designed for industrial use can operate continuously, provided they are correctly specified for the workload. Continuous-duty capability depends on motor rating, pump design, cooling efficiency, and electronic overload protection. Light-duty models are better suited to intermittent operation.
What Is the Difference Between Electronic and Electric Pressure Washers?
All electronic pressure washers are electric-powered, but not all electric pressure washers are electronic. Electronic systems include additional control and protection components that regulate pressure, monitor operating conditions, and protect key components—features typically absent in basic electric washers.
Do Electronic High Pressure Washers Overheat?
Properly designed electronic high pressure washers include thermal protection and load monitoring to prevent overheating. Overheating is usually associated with under-specified equipment, poor ventilation, or incorrect operating conditions rather than the electronic system itself.
What Maintenance Do Electronic High Pressure Washers Require?
Routine maintenance includes pump oil checks, inspection of seals and hoses, and periodic verification of electronic protection systems. Compared to engine-driven machines, electronic systems generally require less maintenance due to fewer moving parts and no fuel-related servicing.
Electronic high pressure washers offer precise pressure control, low noise, and emission-free operation—making them ideal for controlled industrial and commercial environments. Their stable output and integrated safety systems help deliver consistent cleaning results while protecting both surfaces and equipment.
An electronic high pressure washer is the right long-term choice when reliable electrical power is available and cleaning tasks require predictable performance, lower operating costs, and reduced maintenance. For many industrial and municipal applications, these systems provide an efficient, durable, and sustainable cleaning solution over their service life.

Fussen designs electronic high pressure washer systems based on a deep understanding of pump mechanics, pressure–flow balance, and continuous-duty operation. Each system is engineered with industrial-grade electric motors, durable plunger pumps, and integrated electronic protection to deliver stable performance in demanding cleaning environments.
Rather than offering one-size-fits-all machines, Fussen supports application-matched system configuration, ensuring pressure levels, flow rates, power supply, and accessories are aligned with real operating conditions. This approach allows Fussen electronic high pressure washer systems to perform reliably across industrial cleaning, municipal maintenance, and professional cleaning applications where long service life and operational stability are critical.